Data obtained from The Global Cancer Observatory (GCO) reports that cancer is currently one of the most serious diseases throughout the world. There are nearly 20 million new cancer cases and almost 9.6 million deaths.
Besides an extensive range of genetic and epigenetic alterations, components of the tumor microenvironment tend to exert a significant impact on tumor progression.
The so-called tumor microenvironment (TME) is known to be the environment around the tumor and includes the encircling blood vessels, fibroblasts, signaling molecules, immune cells and the extracellular matrix (ECM).
Such cellular and non-cellular components of TME have the ability to reprogram the processes of tumor emergence and development by controlling various cascade signaling pathways.
Therefore, gaining better insights into the basic cellular and molecular mechanisms controlling these interactions could be an innovative strategy to interrupt cancer development and add up to the development of effective and safe therapeutic strategies to combat cancer.
At present, the TME has turned out to be a hot area for antibody drug development and cancer treatment. ACROBiosystems has come up with a range of TME-related targets, like TGF-β, Notch, etc., supporting cancer treatment and accelerating the R&D procedure of users.
Hot targets
- Foster angiogenesis and migration in TME
- Cytokines exhibiting pleiotropic biological activities
- Suppress immune system by controlling the function of immune cell groups in the TME
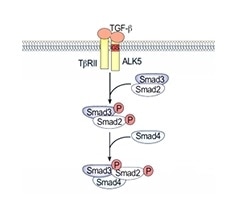
Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
- Control the cell differentiation, proliferation, apoptosis and cell boundary formation
- High expression in malignant tumors
- Communication with FGF and Wnt signaling pathways, maintain cancer stem cell (CSC) growth and reshape the TME
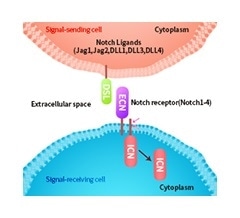
Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
- Play a vital role in tumor angiogenesis, metastasis and progression
- Cell adhesion molecules
- Cell adhesion receptor with the function of signal transduction
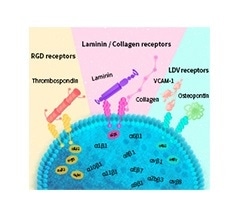
Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
- Have a vital role in fostering angiogenesis and regeneration
- A potent angiogenic factor
- Feature other multiple functions like immune regulation and neuroprotection
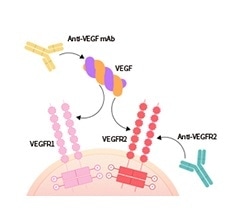
Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Product Features
- High purity verified by MALS
- Different tags and species can be chosen
- High bioactivity verified by SPR/BLI/ELISA/FACS, etc.
Targets of Integrin signaling pathways
Source: ACROBiosystems
Targets of Integrin signaling pathways
| Integrin alpha 10 beta 1 |
Integrin alpha 11 beta 1 HOT |
Integrin alpha 1 beta 1 |
Integrin alpha 2b beta 3 |
Integrin alpha 2 beta 1 |
| Integrin alpha 3 beta 1 |
Integrin alpha 4 beta 1 |
Integrin alpha 4 beta 7 HOT |
Integrin alpha 5 beta 1 |
Integrin alpha 6 beta 1 |
| Integrin alpha 8 beta 1 |
Integrin alpha 9 beta 1 |
Integrin alpha D beta 2 |
Integrin alpha E beta 7 |
Integrin alpha L beta 2 |
| Integrin alpha M beta 2 |
Integrin alpha V beta 1 HOT |
Integrin alpha V beta 3 HOT |
Integrin alpha V beta 5 HOT |
Integrin alpha V beta 6 HOT |
| Integrin alpha V beta 8 |
Integrin alpha X beta 2 |
Integrin beta 8 |
Integrin isoform alpha-7X2B beta 1 |
|
Targets of TGF-β signaling pathways
| LAP (TGF-beta 1) |
Latent TGF-beta 1 |
TGF-beta 1 HOT |
TGF-beta 2 |
TGF-beta 3 |
| TGF-beta RII HOT |
|
|
|
|
Targets of Notch signaling pathways
| NOTCH1 |
NOTCH2 |
NOTCH3 |
DLL1 |
DLL3HOT |
| DLL4 |
Jagged 1 |
Thrombospondin-2 |
Netrin receptor DCC |
Netrin-1 |
Targets of VEGF signaling pathways
| VEGF110 |
VEGF120 |
VEGF121 |
VEGF164 |
VEGF165 HOT |
| VEGF-B |
VEGF-C HOT |
VEGF-D |
VEGF R1 |
VEGF R2 |
| VEGF R3 |
|
|
|
|
Targets of other important signaling pathways
| EGF |
EGF R HOT |
EGFRvIII |
HGF |
HGF R |
| wnt |
FGF |
hedgehog |
|
|
Assay Data
High purity — MALS verified
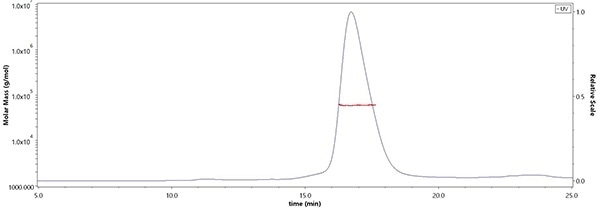
The purity of Human DLL3, His Tag (Cat. No. DL3-H52H4) was more than 95% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 55–65 kDa verified by SEC-MALS. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
High bioactivity — ELISA
TGF-beta 1 (TG1-H4212)
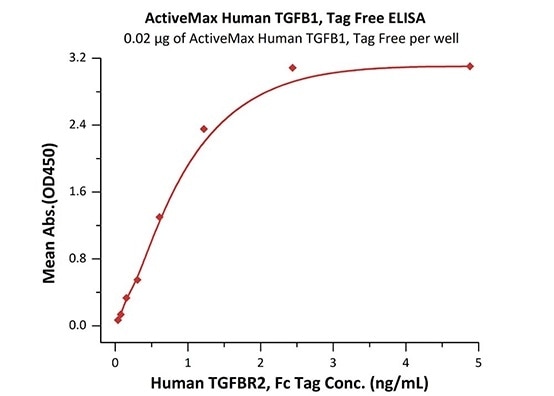
Immobilized ActiveMax® Human TGFB1, Tag Free (Cat. No. TG1-H4212) at 0.2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human TGFBR2, Fc Tag (Cat. No. TG2-H5252) with a linear range of 0.08-1 ng/mL (QC tested). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
High bioactivity —BLI
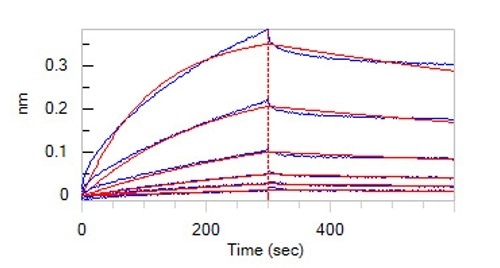
Loaded Human NOTCH2, Fc Tag (Cat. No. NO2-H5255) on Protein A Biosensor, can bind Human DLL4, His Tag (Cat. No. DL4-H5227) with an affinity constant of 77.6 nM as determined in BLI assay (ForteBio Octet Red96e) (Routinely tested). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
High bioactivity —SPR
HGF R (MET-H5256)
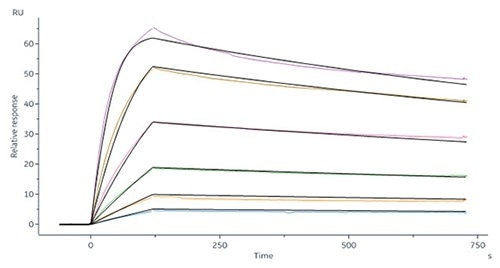
Human HGF R Protein, Fc Tag (Cat. No. MET-H5256) captured on CM5 chip via Anti-human IgG Fc antibodies surface can bind Human HGF Protein, His Tag (Cat. No. HGF-H52H3) with an affinity constant of 75.2 pM as determined in an SPR assay (Biacore 8K) (QC tested). Image Credit: ACROBiosystems