Neurodegeneration is a neurological condition characterized by progressive atrophy and permanent neuronal damage. Two of the most prevalent neurodegenerative disorders are Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD).
GDNF, NGF, and BDNF are growth factors that help neurons survive, maintain, and regenerate, making them potential therapies for neurodegenerative illnesses.
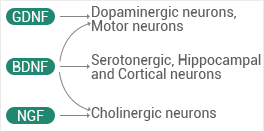
Figure 1. Neuron Specificity Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Clinical studies for GDNF (a treatment for Parkinson’s disease), NGF (a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease), and BDNF (a treatment for both AD and PD) are now underway.
Huntington’s disease (HD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and Rett syndrome are among the less frequent neurodegenerative illnesses that potentially benefit from therapies targeting neurotrophic factors and related receptors.
Neurotrophins are growth factors required for neuron survival, development and maintenance. NGF, BDNF, neurotrophin 3, and neurotrophin 4 are members of the neurotrophin family.
They can induce neurotrophic or pro-apoptotic signaling by binding to certain Trk receptors with high affinity and p75NTR with low affinity, respectively. NGF attaches to TrkA, while BDNF and neurotrophin 4 attach to TrkB and TrkC, respectively.
In Alzheimer’s disease, NGF, BDNF, and all receptors are candidates for treatment. BDNF can potentially be used to treat Parkinson’s disease.
NGF (nerve growth factor)
NGF is the first member of the neurotrophin family to be found. Specific neurons rely on it for life, development and maintenance.
Human NGF protein
11050-HNAC
- Expressed Host: CHO Stable Cells
- Activity: TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells were used in a cell proliferation experiment.
- Purity: >95%
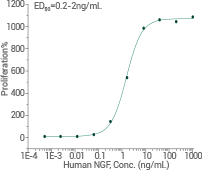
Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
BDNF (brain derived neurotrophic factor)
Sensory neurons, retinal ganglia, some cholinergic neurons, spinal motor neurons, and certain dopaminergic neurons all benefit from BDNF.
Mouse BDNF Protein
50240-M08H
- Purity: >95%
- Expressed Host: HEK293 Cells

Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Neurotrophin 3/NT3
Human NT3 Protein
- Expressed Host: E. coli
- Activity: Binding capacity to human TrkB in a functional ELISA.
- Purity: > 90%
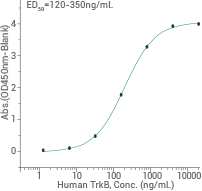
Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Neurotrophin 4/NT4
10265-HNAE
- Purity: >95%
- Expressed Host: HEK293 Cells
Trk receptors
Table 1. Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| Cat# |
Molecule |
Species |
Expressed Host |
Purity |
Tag |
Activity |
| 11073-H03H |
TrkA |
Human |
HEK293 Cells |
>98% |
C-hFc & His |
Active |
| 11073-H07E1 |
TrkA |
Human |
E. coli |
>97% |
N-His |
Active |
| 51103-M02H |
TrkA |
Mouse |
HEK293 Cells |
>90% |
C-hFc |
Active |
| 51103-M08H |
TrkA |
Mouse |
HEK293 Cells |
>95% |
C-His |
Active |
| 70101-D01H |
TrkA |
Canine |
HEK293 Cells |
>90% |
N-hFc |
Active |
| 70101-D07H |
TrkA |
Canine |
HEK293 Cells |
>95% |
N-His |
Active |
| 80404-R02H |
TrkA |
Rat |
HEK293 Cells |
>95% |
C-hFc |
Active |
| 80404-R08H |
TrkA |
Rat |
HEK293 Cells |
>95% |
C-His |
Active |
| 10047-H03H |
TrkB |
Human |
HEK293 Cells |
>90% |
C-hFc & His |
Active |
| 10047-H08H |
TrkB |
Human |
HEK293 Cells |
>97% |
C-His |
Active |
| 50132-M08H |
TrkB |
Mouse |
HEK293 Cells |
>98% |
C-His |
Active |
| 70035-D08H |
TrkB |
Canine |
HEK293 Cells |
>95% |
C-His |
Active |
| 80243-R08H |
TrkB |
Rat |
HEK293 Cells |
>95% |
C-His |
Active |
| 10048-H03H |
TrkC |
Human |
HEK293 Cells |
>98% |
C-hFc & His |
Active |
| 10048-H08H |
TrkC |
Human |
HEK293 Cells |
>95% |
C-His |
Active |
| 50320-M08H |
TrkC |
Mouse |
HEK293 Cells |
>95% |
C-His |
Active |
Low affinity common receptor to neurotrophins: p75NTR
Human p75NTR Protein
13184-H02H
- Purity: >95%
- Expressed Host: HEK293 Cell
- Activity: ED50 is 0.5–3 g/mL in the presence of 4 ng/mL Recombinant Human NGF and inhibits NGF-dependent proliferation of TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells.
Mouse p75NTR Protein
50971-M02H
- Purity: >90%
- Expressed Host: HEK293 Cell
- Activity: TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells’ NGF-dependent proliferation is inhibited. When 2 ng/mL recombinant mouse NGF is present, the ED50 is 0.5–3 g/mL.
GDNF, or glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor, is important for motor neuron survival and axon expansion. It is being tested in clinical studies as a possible treatment for Parkinson’s. Drugs similar to GFL are under development to treat neuropathic pain and addiction.
The GDNF family of ligands (GFLs) also includes neurturin (NRTN), artemin (ARTN), and persephin (PERS) (PSPN). These compounds bind to the proteins GFRA1, GFRA2, GFRA3, and GFRA4.
The activation of the RET tyrosine kinase receptor by the GDNF/GFRA1 complex leads to cell survival, proliferation and development via the MAPK/ERK or PI3K/Akt pathways. GDNF/GFRA1 also binds to NCAM and causes axonal growth. GDNF can also work in tandem with other growth factors, such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta).
Sino Biological has created recombinant GDNF and GFRA1 proteins and antibodies from a variety of animals, including humans, mice, cynomolgus, rabbits, rats and dogs.
GDNF is an important factor in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. As a common signaling receptor shared by GDNF family ligands, GDNF binds to GFR1 and Ret protein. Sino Biological has created bioactive recombinant growth factors from human, mouse, cynomolgus, rhesus, rat, and canine species.
Recombinant GDNF and GFRA1 proteins
Human GDNF protein
10561-HNCH
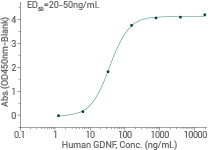
Binding ability by ELISA. Immobilized human GFRA1 (Cat:10330-H02H) at 10 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind GDNF. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Rat GDNF protein
80050-R07B
- Purity: >95%
- Expressed Host: Insect Cell
- Activity:
- Bind rat GFRA1
- Cell Proliferation
Canine GDNF protein
70255-D01H
- Purity: >90%
- Expressed Host: HEK293 Cell
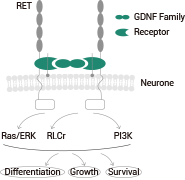
Figure 2. GDNF ligand dimer binds to two GFRα receptors and dimerizes two RET receptors. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
More GFRα1 proteins
Table 2. Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| Cat# |
Species |
Expressed Host |
Tag |
Purity |
Activity |
| 10330-H02H |
Human |
HEK293 Cells |
hFc |
>90% |
Active |
| 10330-H08H |
Human |
HEK293 Cells |
His |
>98% |
Active |
| 50171-M08H |
Mouse |
HEK293 Cells |
His |
>98% |
Active |
| 70062-D08H |
Canine |
HEK293 Cells |
His |
>95% |
|
| 80021-R02H |
Rat |
HEK293 Cells |
hFc |
>90% |
Active |
| 80021-R08H |
Rat |
HEK293 Cells |
His |
>97% |
Active |
Other related proteins
- ARTN
- GFRA2
- GFRA3
- RET
- NCAM
- TGF-beta
Antibodies for GDNF and GFRA1
Sino Biological has created a GDNF and GFRA1 antibody panel that can be utilized in WB, IF, ELISA, and ICC.
Anti-GFRA1 rabbit monoclonal antibody
(Cat#: 50171-R009)
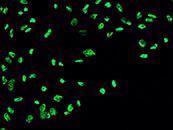
Immunofluorescence Staining of GDNF in U251MG Cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Anti-GFRA1 rabbit monoclonal antibody
(Cat#: 50171-R009)
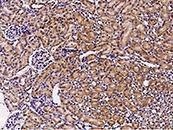
Immunochemical Staining of Mouse GFRA1 in Mouse Kidney Cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
GDNF superfamily & receptors
In the embryonic and adult central nervous systems, GDNF superfamily proteins (artemin/ARTN, neurturin/NRTN, and persephin/PSPN) have protective and restorative actions (CNS). GFR1, GFR2, GFR3, and GFR4 are bounded by GDNF, Neurturin, Artemin, and Persephin, respectively.