Consumer Medicine Information (CMI) summary
The
full CMI on the next page has more details. If you are worried about using this medicine,
speak to your doctor or pharmacist.
Why am I using Actemra?
Actemra contains the active ingredient tocilizumab. Actemra for subcutaneous injection
is used to treat active moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and giant cell
arteritis (GCA) in adults, active moderate to severe polyarticular juvenile idiopathic
arthritis (pJIA) in children over 2 years of age and active systemic juvenile idiopathic
arthritis (sJIA) in children and adolescents, aged 1 year and over. For more information,
see Section
1. Why am I using Actemra? in the full CMI.
What should I know before I use Actemra?
Do not use if you have ever had an allergic reaction to Actemra or any of the ingredients
listed at the end of the CMI.
Talk to your doctor if you have any other medical conditions, take any other medicines,
or are pregnant or plan to become pregnant or are breastfeeding.
What if I am taking other medicines?
How do I use Actemra?
Follow all instructions given to your doctor or pharmacist carefully. They may differ
from the information contained in this leaflet. Use Actemra exactly as your doctor
has prescribed.
The recommended dose of Actemra is dependent on your weight and depends on what you
are being treated for.
What should I know while using Actemra?
|
Things you should do
|
Tell your doctor immediately or go to accident and emergency if you develop symptoms
of an allergic reaction.
Tell your doctor immediately if you develop an infection or have symptoms of an infection
while you are using Actemra.
Tell your doctor if you become pregnant or if you are breast-feeding while taking
Actemra.
If you are a woman of childbearing potential, you should use adequate contraception
during and for several months after treatment with Actemra.
|
|
Driving or using machines
|
Be careful driving or operating machinery until you know how Actemra affects you.
|
|
Looking after your medicine
|
Store in a refrigerator (2°C to 8°C). Do not freeze.
The pre-filled syringe must always be kept in the carton to protect from light and
keep dry.
Once removed from the refrigerator, the pre-filled syringe can be stored up to 2 weeks
(14 days) at or below 30°C.
|
Are there any side effects?
Serious side effects include the following: allergic reactions such as chest tightness, wheezing, difficulty breathing, severe dizziness or light-headedness,
swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat with difficulty breathing, skin rash, itching
or hives (raised red patches of skin that are often very itchy), signs of an infection with or without fever, signs of tears of the stomach or intestines, liver disease, hepatitis and/or jaundice, signs of pancreatitis.
Active ingredient:
tocilizumab (rch)
Consumer Medicine Information (CMI)
This leaflet provides important information about using Actemra. You should also speak to your doctor or pharmacist if you would like further information
or if you have any concerns or questions about using Actemra.
Where to find information in this leaflet:
Why am I using Actemra?
Actemra contains the active ingredient tocilizumab.
Actemra belongs to a group of medicines called monoclonal antibodies.
Monoclonal antibodies are proteins which specifically recognise and bind to other
unique proteins in the body.
Actemra for subcutaneous injection is used to treat active moderate to severe rheumatoid
arthritis (RA) and giant cell arteritis (GCA) in adults.
Actemra is also used to treat active moderate to severe polyarticular juvenile idiopathic
arthritis (pJIA) in children over 2 years of age and active systemic juvenile idiopathic
arthritis (sJIA) in children and adolescents, aged 1 year and over. Some of the signs
and symptoms of these conditions are caused by the actions of a protein called interleukin-6
receptor (IL-6R).
Actemra works by binding and blocking IL-6R thereby helping to relieve some of the
signs and symptoms of these conditions. For patients with RA, Actemra can also prevent
damage occurring to your joints.
There are different types of medicines used to treat RA, GCA, pJIA and sJIA. Your
doctor, however, may have prescribed Actemra for another purpose.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why Actemra has been prescribed for
you.
Actemra is not addictive.
This medicine is available only with a doctor's prescription.
What should I know before I use Actemra?
Warnings
Do not use Actemra if:
Actemra, any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet, or any other recombinant
human or humanised antibodies or proteins that are of hamster origin
Always check the ingredients to make sure you can use this medicine.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
chest tightness, wheezing or difficulty breathing
severe dizziness or light-headedness
swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat or other parts of the body with difficulty
breathing
skin rash, itching or hives (raised red patches of skin that are often very itchy)
or
2.
you have an active, severe infection
Actemra can reduce your body's ability to respond to infections and may make an existing
infection worse or increase the chance of getting a new infection. This may be important
if you have diabetes or diverticulitis (which increase your risk of infection).
Tell your doctor if you think you have an infection or have symptoms of an infection.
Signs of an infection, with or without fever include:
sweating or chills,
feeling very tired
cough
shortness of breath
muscle aches
weight loss
warm, red, or painful skin or sores on your body
blood in phlegm
diarrhoea or stomach ache
persistent headaches
burning when you urinate or urinating more often than normal.
Check with your doctor if:
you have any other health problems, especially the following:
liver disease such as viral hepatitis or other liver problems
Your doctor will monitor your liver function closely before and during your treatment
with Actemra.
HIV or AIDs
tuberculosis
diverticulitis or ulcers in your intestine
a low white blood cell count (white blood cells that help the body fight off infections)
a low platelet count (blood cells that help with blood clotting and stop bleeding)
diabetes
cancer
heart problems
raised blood pressure
high cholesterol or triglycerides
kidney disease
have a condition which affects your nervous system, such as multiple sclerosis or
neuropathy
you are planning to have a vaccination or have recently had a vaccination
Certain types of vaccines should not be given while using Actemra.
During treatment, you may be at risk of developing certain side effects. It is important
you understand these risks and how to monitor for them. See additional information
under Section
6. Are there any side effects?
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant.
Women of childbearing potential should be advised to use adequate contraception during
and for several months after treatment with Actemra. Actemra should not be used during
pregnancy as Actemra may harm your unborn baby. However if there is a need to take
Actemra when you are pregnant, your doctor will discuss the benefits and risks to
you and the unborn baby.
Tell your doctor if you are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed
It is not known whether Actemra passes into breast milk. It is recommended that you
discontinue breast-feeding while you are treated with Actemra.
Use in Children
Actemra given as a subcutaneous injection to patients below 18 years of age with conditions
other than pJIA and sJIA has not been studied.
Actemra given as a subcutaneous injection in pJIA in children under the age of 2 and
sJIA in children under the age of 1 has not been studied.
Actemra must not be given to children weighing less than 10 kg.
What if I am taking other medicines?
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines, including any
medicines, vitamins or supplements that you buy without a prescription from your pharmacy,
supermarket or health food shop.
These medicines increase your risk of side effects with Actemra:
other biological medicines for RA. e.g. infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept, certolizumab pegol, golimumab anakinra,
abatacept, rituximab.
It is unknown how Actemra interacts with these medicines. You may have an increased
risk of infection. You should not use Actemra with other biological medicines for
RA.
vaccines
Certain types of vaccines should not be given while receiving Actemra. You may have
an increased risk of infection.
Actemra may reduce the amount of some medicines that require close monitoring to ensure drug levels are maintained. You may need to use different amounts of your
medicine, or you may need to take different medicines. Your doctor will advise you.
E.g.:
warfarin, a medicine used to prevent blood clots
cyclosporin, a medicine used after organ transplants
atorvastatin and simvastatin, medicines used to reduce cholesterol levels
calcium channel blockers, such as amlodipine, which are used to treat raised blood
pressure
theophylline, a medicine used to treat asthma
phenytoin, a medicine used to treat convulsions
benzodiazepines, such as diazepam, which are used to treat anxiety
Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure about what medicines, vitamins
or supplements you are taking and if these affect Actemra.
How do I use Actemra?
Follow all instructions given to your doctor or pharmacist carefully. They may differ
from the information contained in this leaflet. Use Actemra exactly as your doctor
has prescribed.
How much to inject
Adult patients with RA and GCA
The recommended dose of Actemra to treat RA or GCA is 162 mg injected once a week.
For GCA, your doctor may prescribe a lower dose of 162 mg every 2 weeks.
Actemra must be used on the same day each week. Choose the day of the week that best
fits your schedule.
The syringe is designed to deliver 162 mg per injection when used according to the
instructions in this leaflet.
Your doctor will test your blood to help guide your treatment. If you experience certain
changes in your blood tests, your doctor may decide to reduce the frequency of dosing
to 162 mg every 2 weeks.
For RA, Actemra is usually given in combination with methotrexate (MTX). However you
may use Actemra on its own if your doctor determines that initial treatment with MTX
is inappropriate or unsuccessful.
For GCA, Actemra is initially given in combination with a glucocorticoid medicine
(such as prednisone). Over the period of treatment, deding on your response to Actemra,
your doctor will adjust the dose of the glucocorticoid with the aim to reduce it over
time.
Children and adolescents with pJIA or sJIA (aged 12 and over)
The usual dose of Actemra depends on the patient's weight.
|
Children and adolescents with pJIA (aged 1 and over)
|
|
If the patient weighs less than 30 kg
|
The dose is 162 mg (the content of 1 pre-filled syringe) once every 3 weeks
|
|
If the patient weighs 30 kg or more
|
The dose is 162 mg (the content of 1 pre-filled syringe) once every 2 weeks
|
|
Children and adolescents with sJIA (aged 1 and over)
|
|
If the patient weighs less than 30 kg
|
The dose is 162 mg (the content of 1 pre-filled syringe) once every 2 weeks
|
|
If the patient weighs 30 kg or more
|
The dose is 162 mg (the content of 1 pre-filled syringe) once every week
|
Actemra must not be given to children less than 10 kg.
The increasing body weight of a child initially under 30kg should be checked regularly.
This is because there is a risk of underdose for this medicine if the frequency of
administration does not increase from every 3 weeks to every 2 weeks for pJIA patients
(or every 2 weeks to once every week for sJIA patients) as the child grows from under
to over 30 kg body weight.
How to inject Actemra
Actemra is administered by subcutaneous injection. This means it is injected with
a short needle into the fatty tissue just under the skin.
Serious allergic reactions can occur with Actemra injections.
At least the first injection of Actemra will be given under the supervision of your
healthcare provider in a healthcare facility that can manage these reactions. After
your first injection, your doctor may discuss with you whether it would be appropriate
for you to inject the next Actemra injection yourself at home, in which case, you
or a caregiver would be instructed on how to give the injection and what to do if
you experience symptoms of an allergic reaction.
Directions for self-injection
You should read these directions from beginning to end before starting to inject so
that you are familiar with each step of the procedure. These instructions must be
carefully followed. Consult with your healthcare provider if you require further instructions.
These instructions do not replace the instructions from your healthcare provider.
Your healthcare provider should show you how to prepare and inject properly before
you inject for the first time. Ask them any questions you may have.
Do not attempt to administer an injection until you are sure that you understand how
to self-inject.
It is important to remain under your doctor's care while using Actemra. It is recommended
you have someone else present when you self-inject Actemra in case you experience
any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction described under
Section 5. What should I know while using Actemra?.
The syringe is for single use only and should be safely discarded after use.
How to inject using the syringe
The syringe components:
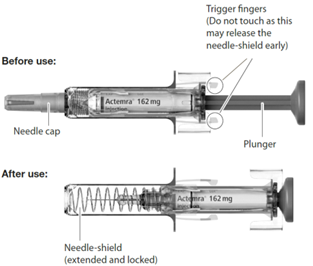
Do not use if the syringe appears to be damaged.
Do not use if the medicine is cloudy, hazy, discoloured or contains particles.
Do not shake the syringe.
Do not try to open the syringe or take it apart.
Do not remove the needle cap until you are ready to inject.
Do not inject through clothing covering the skin.
Do not re-use the same syringe.
Do not touch the syringe trigger fingers as this may damage the syringe.
Gather what you will need:
|
Included in the pack
|
Pre-filled syringe
|
|
Not included in the pack
|
Alcohol pad
Sterile cotton ball or gauze
Puncture-resistant container (also called a "sharps" container) for safe disposal
of the needle cap and used syringe.
|
Find a well-lit, clean, flat surface such as a table.
Step 1. Visually check the syringe
Take the carton containing the syringes out of the refrigerator and remove one syringe
from the carton. Return the remaining syringes in the carton to the refrigerator.
Do not shake.
If there is foam in the medicine, put the syringe back in the carton in the refrigerator
for use another time and take a new syringe from the refrigerator.
Visually examine the syringe, as well as the medicine through the viewing window.
The injection should be clear and colourless or slightly yellow.
Do not use if the syringe appears to be damaged.
Do not use if the medicine is cloudy, hazy, discoloured or contains particles.
Check the expiration date on the carton and syringe to make sure that it has not expired.
The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
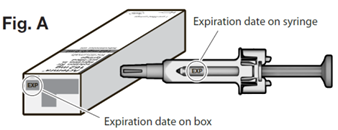
Do not use the syringe if the expiration date has passed.
Do not remove the syringe needle cap until step 5.
Step 2. Allow the syringe to adjust to room temperature
Place the syringe on a clean flat surface. Allow the syringe to warm up to room temperature
which should take 25 to 30 minutes.
Do not warm up the syringe in any other way.
Step 3. Clean your hands
Wash your hands with soap and water. Cleanliness is vital during the injection procedure.
Step 4. Choose and prepare an injection site
The front of your thigh or your abdomen below the navel (belly button), except for
the 2-inch (5 cm) area around your navel are the recommended injection sites (See
Figure B). If a caregiver is giving the injection, the outer area of the upper arms
may also be used.
Use a different place each time you give yourself an injection. The new injection
site should be at least 3 centimetres away from your previous injection site.
Fig. B
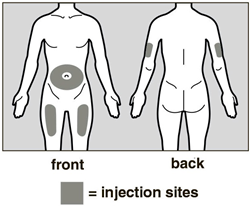
Do not inject into areas that could be irritated by a belt or waistband. Do not inject
into moles, scars, bruises, or areas where the skin is tender, red, hard or not intact.
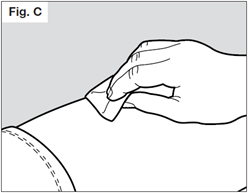
Clean the chosen injection area using the alcohol pad, to reduce the risk of infection.
Let the skin dry for approximately 10 seconds. Be sure not to touch the cleaned area
prior to the injection. Do not fan or blow on the cleaned area.
Step 5. Remove needle cap
Do not hold the syringe by the plunger while removing the needle cap.
Hold the needle shield of the syringe firmly with one hand and pull off the needle
cap with the other hand. If you cannot remove the needle cap you should request the
help of a caregiver or contact your healthcare provider.
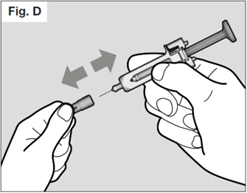
Do not touch the needle or let it touch any surface.
You may see a drop of liquid at the end of the needle. This is normal and will not
affect your dose.
There may be a small air bubble in the ACTEMRA pre-filled syringe. You do not need
to remove it.
Throw away the needle cap in the sharps container.
Once the needle cap is removed, the syringe should be used immediately, to prevent
the medicine from drying out and blocking the needle. If it is not used within 5 minutes,
the syringe should be disposed of in the sharps container and a new syringe should
be used.
Do not re-attach the needle cap after removal.
Step 6. Give the injection
Hold the syringe comfortably in your hand. Be careful not to touch the syringe trigger
fingers as this may damage the syringe.
To be sure the needle can be inserted correctly under the skin, pinch a fold of loose
skin at the clean injection site with your free hand.
Do not hold or push on the plunger while inserting the needle into the skin.
Insert the needle all the way into the pinched skin at an angle between 45° to 90°
with a quick, firm action.
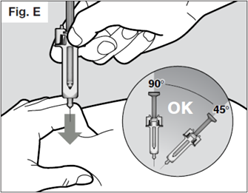
It is important to choose the correct angle to ensure the medication is delivered
under the skin (into fatty tissue), otherwise the injection could be painful and the
medication may not work.
Then keep the syringe in position and let go of the pinch of skin.
Hold the syringe with two fingers under the flange (or "wings") and thumb on the plunger.
Slowly inject all of the medicine by gently pushing the plunger all the way down.
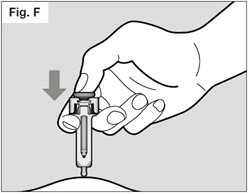
You must press the plunger all the way down to ensure that you get the full dose of
medication and to ensure the trigger fingers are completely pushed to the side.
If the plunger is not fully depressed the needle shield will not extend to cover the
needle when it is removed.
Once the plunger is pushed all the way down, keep pressing down on the plunger to
be sure all of the medicine is injected before taking the needle out of the skin.
Keep pressing down on the plunger while you take the needle out of the skin at the
same angle as inserted.
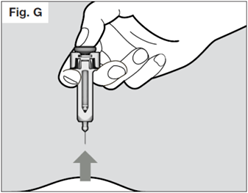
Once the needle is removed completely from the skin, you can release the plunger.
The needle will retract allowing the needle shield to protect the needle.
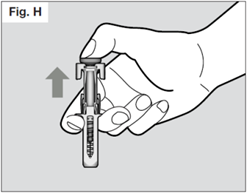
If the needle is still exposed proceed carefully, and place the syringe into the sharps
container to avoid injury with the needle (see Step 7).
If you see drops of blood at the injection site, you can press the sterile cotton
ball or gauze over the injection site for approximately 10 seconds.
Do not rub the injection site.
Step 7. Safely dispose of the syringe
Do not try to re-cap your syringe.
Throw away used syringes in a sharps container.
Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about where you can get
a sharps container or what other types of puncture-resistant containers you can use
to safely dispose of your used syringes, if you do not have one.
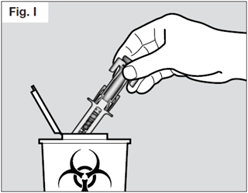
Do not throw away used syringes or the sharps container in household rubbish and do
not recycle them.
Dispose of the full container as instructed by your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Always keep the sharps container out of the reach of children.
When to use Actemra
The duration of treatment depends on how you are responding to the medicine. Your
doctor will discuss this with you. Continue to use Actemra until your doctor tells you to stop.
If an adult with RA/GCA or a child or adolescent with pJIA or sJIA forgets to use
Actemra
It is very important to use Actemra exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Keep track
of your next dose.
|
For once a week Actemra dosing
|
If you missed your once a week Actemra dose and you remember within 7 days, you should
skip the missed dose. Make sure you inject your next dose normally on the next scheduled
day.
For example, if you forget your scheduled dose on Monday but you remember on Wednesday,
you should skip your missed dose and inject the next dose as you would normally on
the following Monday.
|
|
For fortnightly or every three week Actemra dosing
|
If you missed your fortnightly or every three week Actemra dose and you have remembered
within 7 days of the dose you missed, you should inject the missed dose as soon as
possible Inject the next dose as you would on the next scheduled day.
|
Do not give yourself two injections to make up for the injection that you missed.
If it has been more than 7 days since your missed dose, contact your doctor for advice.
If you are not sure when to inject your next dose, contact your doctor for advice.
If you are given too much Actemra
If you think that you or anyone else have had too much Actemra, you may need urgent
medical care. You should immediately:
phone the Poisons Information Centre
(by calling
13 11 26), or
contact your doctor, or
go to the Emergency Department at your nearest hospital.
You should do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning.
What should I know while using Actemra?
Things you must do
Tell your doctor immediately or go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital
if:
you experience symptoms of a serious allergic reaction during or after receiving Actemra such as;
chest tightness, wheezing or difficulty breathing
severe dizziness or light-headedness
swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat or other parts of the body with difficulty
breathing
skin rash, itching or hives (raised red patches of skin that are often very itchy).
The reaction can occur even after multiple doses of Actemra. If you have experienced
any allergic reaction symptoms after using Actemra, do not take the next dose until
you have informed your doctor AND your doctor has told you it is safe to take the
next dose.
Tell your doctor immediately if:
1. You develop an infection or have symptoms of an infection while you are using Actemra. Signs of an infection, with or without fever include:
sweating or chills,
feeling very tired
cough
shortness of breath
muscle aches
weight loss
warm, red, or painful skin or sores on your body
blood in phlegm
diarrhoea or stomach ache
persistent headaches
burning when you urinate or urinating more often than normal.
2. you develop severe blisters and bleeding in the lips, eyes, mouth, nose and genitals while you are using Actemra.
Skin cancer monitoring:
if you are at increased risk for skin cancer:
Regular skin examination is recommended if you are at increased risk for skin cancer.
Exposure to sunlight and UV light should be limited by wearing protective clothing
and using sunscreen with a high protection factor.
Immunosuppressive medication (a medicine that reduces the activity of your immune
system), such as Actemra, have an increased risk of developing skin cancer (melanoma
and non-melanoma).
Tell all doctors, dentists and pharmacists who are treating you that you are receiving
Actemra.
Tell your doctor if you become pregnant while taking Actemra.
Tell your doctor if you are breast-feeding while being treated with Actemra.
Tell your doctor if you feel Actemra is not helping your condition.
Be sure to keep all of your appointments and get follow-up blood tests done as ordered by your doctor so that your progress can be checked.
Blood tests/monitoring:
Liver enzymes:
If you have rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or giant cell arteritis (GCA), your doctor should
do blood tests every 4 to 8 weeks for the first 6 months of treatment followed by
every 12 weeks. Your doctor will then decide on the frequency.
If you have polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA) or systemic juvenile
idiopathic arthritis (sJIA), your doctor should do blood test at the time of second
administration and every 4 to 8 weeks for pJIA and 2 to 4 weeks for sJIA.
Blood count:
If you have rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or giant cell arteritis (GCA), your doctor should
do blood tests every 4 to 8 weeks after the start of therapy. Your doctor will then
decide on the frequency.
If you have polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA) or systemic juvenile
idiopathic arthritis (sJIA), your doctor should do blood tests at the time of second
administration and every 4 to 8 weeks for pJIA and 2 to 4 weeks for sJIA.
Your doctor should do blood test levels according to the current clinical guidelines.
Cholesterol:
If you have RA and sJIA, your doctor will decide on the frequency of testing.
If you have pJIA, your cholesterol levels should be tested every 3 months while on
Actemra.
Remind any doctor, dentist or pharmacist you visit that you are using Actemra.
Driving or using machines
Be careful driving or operating machinery until you know how Actemra affects you.
Actemra has not been shown to impair the ability to drive or operate machinery. However
if you experience dizziness, a reported side effect, then you should not drive or
operate machinery until it has resolved.
Looking after your medicine
Before injection
Store in a refrigerator (2°C to 8°C). Do not freeze.
Store the syringes in the carton to protect them from light and to keep them dry.
Once removed from the refrigerator, the pre-filled syringe can be stored up to 2 weeks
(14 days) at or below 30°C. The unopened pre-filled syringe may be removed and returned
to the refrigerator multiple times as long as the total length of time at or below
30°C is not more than 14 days. The pre-filled syringe must always be kept in the carton
to protect from light and keep dry.
Do not use Actemra if the package is torn or shows signs of tampering.
Do not use Actemra after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and syringe
labels after 'EXP'. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
After injection
The syringe is intended for single use only and must be discarded after the injection.
Dispose of the syringes in a sharps container as instructed by your doctor, nurse
or pharmacist.
Do not put the used syringes in your normal household rubbish.
Keep it where young children cannot reach it.
Getting rid of any unwanted medicine
If you no longer need to use this medicine or it is out of date or if your doctor
tells you to stop using Actemra, take it to any pharmacy for safe disposal. Do not
use this medicine after the expiry date.
Are there any side effects?
All medicines can have side effects. If you do experience any side effects, most of
them are minor and temporary. However, some side effects may need medical attention.
See the information below and, if you need to, ask your doctor or pharmacist if you
have any further questions about side effects.
Less serious side effects
|
Less serious side effects
|
What to do
|
|
Blood pressure related:
high blood pressure or hypertension (symptoms may include headache, dizziness, ringing
in the ears)
Injection site reaction related:
skin redness
itchy skin
pain in the injection site
Stomach related:
constipation
General:
anxiety
difficulty sleeping
low potassium levels shown by blood tests
mouth ulcers
|
Speak to your doctor if you have any of these less serious side effects and they worry
you.
|
Serious side effects
|
Serious side effects
|
What to do
|
|
Allergic reaction related:
chest tightness, wheezing or difficulty breathing,
severe dizziness or light-headedness
swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat or other parts of your body with difficulty
breathing
skin rash, itching or (raised red
patches of skin that are often very itchy).
Infections:
signs of an infection, with or without fever: sweating or chills, feeling very tired,
cough, shortness of breath, muscle aches, weight loss, warm, red, or painful skin
or sores on your body, blood in phlegm, diarrhoea or stomach ache, persistent headaches,
burning when you urinate or urinating more often than normal.
Severe blisters and bleeding in lips, eyes, mouth, nose and genitals.
Stomach and gut:
signs of tears (perforation) of the stomach or intestines such as fever and pain in
the stomach area that does not go away, vomiting blood or material that looks like
coffee grounds, bleeding from your rectum, and a change in your bowel habits
signs of inflamed pancreas (pancreatitis) including: upper stomach pain, abdominal
pain that may spread to the back, generally feeling unwell/sick
Liver:
signs of liver disease, hepatitis and/or jaundice including: nausea, vomiting, loss
of appetite, feeling generally unwell, fever, itching, yellowing of the skin and eyes,
light coloured bowel motions, dark coloured urine.
Laboratory tests:
low white blood cell and platelet counts.
increase in certain liver function tests.
raised blood fat (cholesterol) levels.
|
Call your doctor straight away, or go straight to the Emergency Department at your
nearest hospital if you notice any of these serious side effects.
Call your doctor straight away if you notice any of these serious side effects.
Call your doctor straight away if you notice any of these serious side effects.
Call your doctor straight away if you notice any of these serious side effects.
Make sure you get all your follow-up blood tests done as ordered by your doctor.
|
Side effects in children and adolescents with pJIA and sJIA
Side effects in children and adolescents with pJIA and sJIA are generally similar
to those in adults. Some side effects are seen more often in children and adolescents:
inflamed nose and throat, headache, feeling sick (nausea) and lower white blood cell
counts.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice anything else that may be making you
feel unwell.
Other side effects not listed here may occur in some people.
Reporting side effects
After you have received medical advice for any side effects you experience, you can
report side effects to the Therapeutic Goods Administration online at
www.tga.gov.au/reporting-problems . By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of
this medicine.
Always make sure you speak to your doctor or pharmacist before you decide to stop
taking any of your medicines.
Product details
This medicine is only available with a doctor's prescription.
What Actemra contains
|
Active ingredient
(main ingredient)
|
tocilizumab (rch)
|
|
Other ingredients (inactive ingredients)
|
Actemra
®
(AUST R 234034)
polysorbate 80
histidine
histidine hydrochloride monohydrate
arginine
arginine hydrochloride
methionine
water for injections
Actemra
®
SC (AUST R 370315)
polysorbate 80
histidine
histidine hydrochloride monohydrate
arginine hydrochloride
methionine
water for injections
|
Do not take this medicine if you are allergic to any of these ingredients.
What Actemra looks like
Actemra is a clear to opalescent, colourless to pale yellow solution.
Australian Registration Numbers:
Actemra® 162mg/0.9mL pre-filled syringe AUST R 234034
Actemra® SC 162mg/0.9mL pre-filled syringe AUST R 370315
Actemra is available as a pre-filled pen (162mg/0.9mL) in packs of 1 and 4 pens, with
the tradenames Actemra® and Actemra® SC.
Actemra is also available as a concentrated solution for intravenous infusion.
Who distributes Actemra
Roche Products Pty Limited
ABN 70 000 132 865
Level 8, 30-34 Hickson Road
Sydney NSW Australia
How to contact us

You can also call us on 1800 233 950.
This leaflet is for people in Australia only. If you are not in Australia, you can
contact Roche/Genentech in your country at
www.medinfo.roche.com .
This leaflet was prepared in November 2022.